Light stands as one of the most transformative innovations in human history. In this article, we read about how LED lights work. The journey began with the invention of the incandescent light bulb. Over time, the fluorescent light bulb became the star and replaced the incandescent light bulb.

What do you know about how LED lights work?
How do LED lights work?
What is a diode?
How this led to work:
What is a semiconductor?
What are p type and N type?
What is PN junction?
How do LED strip lights work?
What about digital LED strips?
Advantages of LED Light:
disadvantages of LED:
Light-emitting diode symbol?
What are the advantages of LEDs?
How do LED lights work?
Today, how led lights work? Leed takes the lead, bringing brightness and efficiency together and changing how we see the world. In today’s article, we are How led lights work diving into the fascinating world.
- Of LED lights,
- Their structure,
- And their working functions.
LEDs are versatile and can be found in various types in our daily lives.
Are called through-hole LEDs. This is an LED bulb featuring surface-mounted LEDs inside it. LED stands for light-emitting diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is applied. The process is based on electroluminescence, where the movement of electrons within the semiconductor material generates photons, producing visible light.
What is a diode?
First, we will clarify what this diode is. a is a two-terminal electronic component that allows current to flow in one direction forward biased. This is a diode where the anode is positive and the cathode is negative when connected to a battery with a positive terminal to the anode and the negative terminal to the cathode.
Forward bias current flows easily through the diode; however, if we reverse the battery’s polarity, reverse bias the diode blocks current flow in the opposite direction, maintaining its one-way Behavior: It is primarily made of semiconductor materials such as silicon or germanium. This is a through-hole LED.
How this led to work: How led lights work?
Let’s explore how this led works. It has anode lead and cathode reflective cup. semiconductor die wire Bond lead frame positive terminal and negative terminal.
What is a semiconductor?
Here the semiconductor is the main part; the upper is called p type, and the lower part is called ntype.
What are p type and N type: How led lights work?
Now we have to understand the p type and N type in silicon. There are four valence electrons located in the outermost shell. These valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding with neighboring silicon atoms, forming a crystal lattice structure. in which each silicon atom contributes one electron to each of the four covalent bonds.
It forms with adjacent silicon atoms here; no free electron These are Boron atoms, each having three valence electrons in the outermost shell.
Now if you replace one silicon atom with a boron atom, which has only three valence electrons, there is a deficiency of one electron in the crystal lattice.
This deficiency is referred to as a whole. This type of semiconductor is a p-type semiconductor where positive charge-carrier holes contribute to the electrical conductivity. When a silicon atom is replaced by phosphorus in the crystal lattice, an extra electron is introduced.
Creating a free electron results in an n-type semiconductor. Where free electrons become the dominant charge carriers, contributing to electrical conductivity.
What is PN junction?
When we combine a p-type semiconductor with an N-type semiconductor, we create a PN junction. This is where the p-type and N-type materials meet. If you connect the positive terminal of a voltage source to the p-type material and the negative terminal to the N-type material, this forward biasing reduces the potential barrier at the junction.
Allowing charge carrier holes from the p-type and electrons from the N-type to move across. The junction more easily during this time electrons are released, protons and light emitting.
How do LED strip lights work?
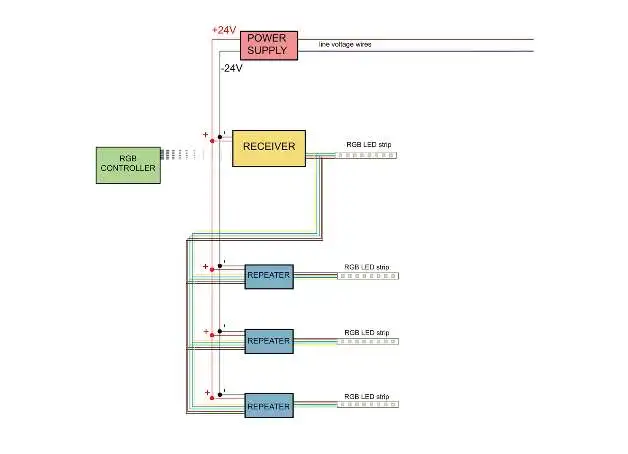
Unbeknownst to most people, there are actually two types of LED strips: Analog and digital LED strips tend to come in one color, with some having the capability of you being able to change what that color is, such as the case with the LED strip I have here from Fantex.
These LED strips require 12 volts to operate and either come with a controller or, in my case, an adapter cable for use with my compatible motherboard The motherboard in my PC, the Asus Z2 70 Maximus 9 Hero, has two headers on the board specifically for use with RGB LED strips.
This is possible due to the fact that the motherboard already runs on 12 volts supplied by the power supply.
Any included controller boxes would also have the capability of converting some other voltage to 12 volts for use with the LED strips. Changes in voltage in each of the three color channels are what allow for RGB strips to display a chosen color zero voltage. yields an off state, while a full 12 volts in each channel would yield white, but
What about digital LED strips?
Well, they’re not too prominent yet since motherboard and case support is a bit scarce at the moment, but there is a company that has been using digital LED strips for quite some time. If you can guess what it is, ten points to you.
NZXT was the answer I was looking for, folks. Their Hue Plus lighting kit contains digital RGB LED strips, and one makes teacher LED strips so much different than their analog cousins is that each LED on the strip is uniquely addressable; in other words, each LED on a strip can be changed to whatever color you want.
These LED strips run on five volts and are not compatible with analog strips or headers. Digitally addressable LED strips do give the user many more options in terms of effects. I used to use the Hue Plus when I was still using the NZXT h4 40 case but decided to move on to a more cohesive LED lighting experience.
The parts I chose to let my case all work with ASUS are ARA software down to the sticks of RAM, and I’m quite content with how it looks, but that may change in the near future.
I’ve been kind of looking at the coolermaster each 500 P, which would also work with my compatible lighting accessories. There may be a case upgrade in the near future.
Advantages of LED Light: How led lights work?

The different advantages of LEDs are their small size and light weight, availability in different spectral colors, long life as compared to lamps, and being easily interfaced with any other electronic circuits. Operating speed is high; it takes only one microsecond to turn on or off LEDs.
disadvantages of LED: How led lights work?
They also have some disadvantages, like needing larger power for their operation. The luminous efficiency of LEDs is low. LEDs get easily damaged due to overcurrent.
Light-emitting diode symbol?
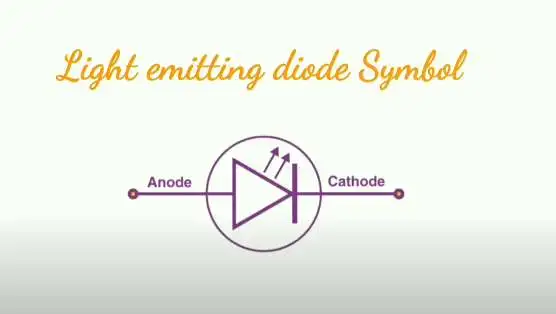
The question is: is a divine light-emitting diode a so-enlightening diode a lighter mating diode? LED is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current flows through it. The added light-emitting diode symbol is the two arrows denoting the emission of light. The figure below shows a simple LED surface [music]. Next, what are the uses of a flight-emitting diode? What are the uses of light-emitting diodes? Below are a few standard LED uses used for TV back lighting used in displays used in automotives. LED used the living of lights.
What are the advantages of LEDs?
They consume less power and require low pressure voltage; no warm-up time is needed for LEDs.
Conclusion: How led lights work?
The Future of LED Technology LED technology has already made significant strides in improving lighting efficiency and sustainability. As research continues, we can expect even more innovations in LED design and applications. From home lighting to advanced displays and medical technologies, LEDs are shaping the future of light.
